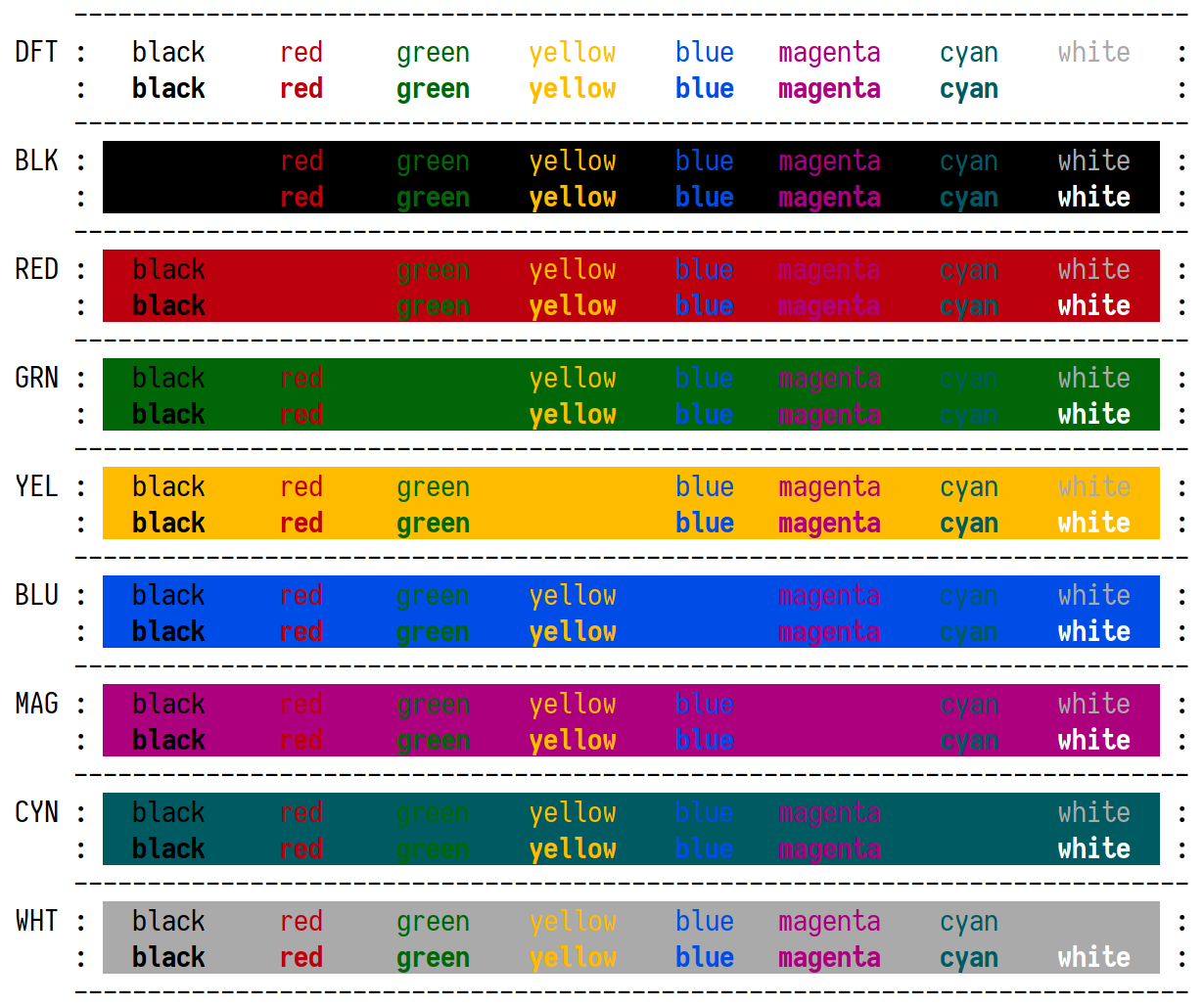
High-contrast terminal color schemes
The goals for both the Contrasty Brightness and Contrasty Darkness color schemes are to provide:
- Legible text
- Distinguishable colors
Contrasty Brightness is particularly useful in very bright environments, e.g. outdoors.
Contrasty Darkness is particularly useful when trying to reduce light emissions while still ensuring enough contrast for text to be legible and colors to be distinguishable, e.g. at night with reduced display brightness.
These color schemes are generated based on Delta E CIE 2000. The color schemes you see here are just two possible solutions that fulfil my preferred constraints.
To generate color schemes based on your own constraints, see Colorschemer on GitHub or the source code below.
Note: Both schemes hide Vim’s “colorcolumn” in buffers that are too narrow. In such buffers the column is placed incorrectly when “wrap” is on.
Contrasty Brightness
- Alacritty
- Vim (Note: Colors are only embedded for Gvim. For Vim to use the same colors, you have to set them in your terminal.)
- .Xresources
# black
color0: #000000
color8: #000000
# red
color1: #bd000d
color9: #bd000d
# green
color2: #006607
color10: #006607
# yellow
color3: #ffbb00
color11: #ffbb00
# blue
color4: #004ce6
color12: #004ce6
# magenta
color5: #ad007f
color13: #ad007f
# cyan
color6: #005a61
color14: #005a61
# white
color7: #aaaaaa
color15: #ffffff
Contrasty Darkness
- Alacritty
- Vim (Note: Colors are only embedded for Gvim. For Vim to use the same colors, you have to set them in your terminal.)
- .Xresources
# black
color0: #000000
color8: #000000
# red
color1: #ff7c4d
color9: #ff7c4d
# green
color2: #22ff00
color10: #22ff00
# yellow
color3: #ffcc00
color11: #ffcc00
# blue
color4: #1a66ff
color12: #1a66ff
# magenta
color5: #ff61df
color13: #ff61df
# cyan
color6: #00ffff
color14: #00ffff
# white
color7: #888888
color15: #ffffff
Source code (Python)
See Colorschemer on GitHub.
License: MIT
"""
Find color schemes with optimally distinct colors using Delta E (CIE2000).
Steps to generate optimal color schemes:
1. Compile list of potential colors.
2. Calculate Delta E between all colors.
3. Compile list of potential schemes with a certain number of colors each.
4. Discard schemes if they contain hues that are too similar or if their
Delta E of any two colors is too low.
5. Output remaining color schemes.
"""
from datetime import datetime
from itertools import combinations
from itertools import zip_longest
from math import factorial
from multiprocessing import cpu_count
from multiprocessing import Lock
from multiprocessing import Manager
from multiprocessing import Pool
from multiprocessing import Value
from colormath.color_conversions import convert_color
from colormath.color_diff import delta_e_cie2000
from colormath.color_objects import HSLColor
from colormath.color_objects import LabColor
from colormath.color_objects import sRGBColor
# Number of colors per scheme
n = 6
# Output formats: 'hex', 'hsl', 'rgb' (0–1) or 'rgb_upscaled' (0–255)
color_codes = ['hex']
# Bright or dark background
bright = True
# Spacing of hues in degrees, smaller spacing results in more potential schemes
# Note: In edge cases larger steps can give slightly better results
# (steps of 1° yield 2899305949260 schemes)
# Factors of 360:
# 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 15, 18, 20, 24, 30, 36, 40, 45, 60
hue_step = 12
# Discard scheme if any hue combination is less than this many degrees apart
min_hue_diff = 12
# Enable to use more RAM for better performance, disable to process larger
# numbers of schemes that will not fit into your RAM
load_schemes_into_ram = False
# Output schemes as soon as they are found
output_schemes_early = False
# Parameters depending on bright or dark background
if bright:
# Approximate hue of highlight color (e.g. background color for matches
# when searching in a man page), can be 'None'
highlight = 60
# Minimum Delta E between the highlight color and the background
min_delta_background_highlight = 20
# Minimum Delta E between all other colors and the background
min_delta_background_color = 50
# Luminance is adjusted this much each step until the required delta to the
# background is achieved
lum_adjust_highlight = -.01
lum_adjust_color = -.01
# Fixed colors, use for example:
# sRGBColor.new_from_rgb_hex('#000000')
# sRGBColor(128, 0, 255, is_upscaled=True)
# sRGBColor(.5, 0, 1)
# HSLColor(0, 0, .8)
# Background
background = sRGBColor.new_from_rgb_hex('#ffffff')
else:
# Approximate hue of highlight color (e.g. background color for matches
# when searching in a man page), can be 'None'
highlight = 240
# Minimum Delta E between the highlight color and the background
min_delta_background_highlight = 20
# Minimum Delta E between all other colors and the background
min_delta_background_color = 50
# Luminance is adjusted this much each step until the required delta to the
# background is achieved
lum_adjust_highlight = .01
lum_adjust_color = .01
# Fixed colors, use for example:
# sRGBColor.new_from_rgb_hex('#000000')
# sRGBColor(128, 0, 255, is_upscaled=True)
# sRGBColor(.5, 0, 1)
# HSLColor(0, 0, .8)
# Background
background = sRGBColor.new_from_rgb_hex('#000000')
# Convert colors
background = convert_color(background, LabColor)
def convert_hue(hue, adjust=lum_adjust_color,
min_delta=min_delta_background_color):
"""Create a color from a hue and adjust its luminance until the Delta E
between the color and the background is sufficient.
"""
color_hsl = HSLColor(hue, 1, .5)
color_lab = convert_color(color_hsl, LabColor)
while True:
if delta_e_cie2000(color_lab, background) < min_delta:
color_hsl.hsl_l += adjust
color_lab = convert_color(color_hsl, LabColor)
else:
return [hue, color_lab]
def calculate_delta(colors):
"""Calculate Delta E between two colors."""
# Structure of dictionary: dict([(hue_1, hue_2): delta_e, ...])
global deltas
deltas[(colors[0][0], colors[1][0])] = \
delta_e_cie2000(colors[0][1], colors[1][1])
def check_scheme(scheme):
"""Check a scheme for similar hues and low Delta E values. Discard if
insufficient.
"""
# Due to lazy evaluation with grouper(), scheme can be None
if not scheme:
return
global lock
# Show progress
global processed
with lock:
processed.value += 1
processed_schemes = processed.value
if processed_schemes % 100000 == 0:
elapsed = datetime.utcnow() - start_time
progress = processed_schemes / total_schemes
print('== Progress: {}/{} {}%'.format(
processed_schemes, total_schemes,
int(round(progress * 100))))
print(' Elapsed time: {}'.format(str(elapsed).split('.')[0]))
print(' Time left: {}'.format(
str(elapsed * (1 / progress) - elapsed).split('.')[0]))
# Check hues
min_hue_diff_scheme = \
min([scheme[i + 1][0] - scheme[i][0] for i in range(5)]
+ [scheme[0][0] + 360 - scheme[-1][0]])
if min_hue_diff_scheme < min_hue_diff:
return
# Check Delta E values
min_delta = 100
global current_min_delta
for x, y in combinations(scheme, 2):
delta = deltas[(x[0], y[0])]
if delta < current_min_delta.value:
return
min_delta = min(min_delta, delta)
new_best = False
notify = False
with lock:
if current_min_delta.value < min_delta:
new_best = True
if int(current_min_delta.value) != int(min_delta):
notify = True
current_min_delta.value = min_delta
if notify:
print('== New minimum Delta E: {}'.format(min_delta))
if new_best and output_schemes_early:
output_scheme(finalize_scheme(
[min_delta, min_hue_diff_scheme, scheme]))
return [min_delta, min_hue_diff_scheme, scheme]
def finalize_scheme(scheme):
"""Finalize a scheme by brightening its highlight color until it reaches
the chosen Delta E to the background and ordering the colors of the scheme.
"""
scheme[2] = list(scheme[2])
hues = [hue for hue, _ in scheme[2]]
# Make sure the first hue is closest to red
if 360 - max(hues) < min(hues):
scheme[2].insert(0, scheme[2].pop())
hues.insert(0, hues.pop())
if highlight:
# Find nearest color to chosen highlight color
highlight_hue = min(hues, key=lambda x: abs(x - highlight))
highlight_pos = hues.index(highlight_hue)
# Adjust luminance of highlight color
color = convert_hue(highlight_hue, lum_adjust_highlight,
min_delta_background_highlight)[1]
# Insert final highlight color into scheme
scheme[2][highlight_pos] = (highlight_hue, color)
return scheme
def color_to_str(color):
"""Return a color’s hex, sRGB or HSL representations."""
s = []
if 'hex' in color_codes:
s.append(str(convert_color(color, sRGBColor).get_rgb_hex()))
if 'rgb_upscaled' in color_codes:
s.append('rgb{}'.format(
str(convert_color(color, sRGBColor).get_upscaled_value_tuple())))
if 'rgb' in color_codes:
s.append('rgb{}'.format(
str(convert_color(color, sRGBColor).get_value_tuple())))
if 'hsl' in color_codes:
s.append('hsl{}'.format(
str(convert_color(color, HSLColor).get_value_tuple())))
return ', '.join(s)
def output_scheme(scheme):
"""Output a color scheme."""
hues = [color[0] for color in scheme[2]]
if scheme[1] - min_hue_diff < hue_step:
print('# Warning: Scheme borders minimal hue difference')
print('# Minimum Delta E: {}'.format(scheme[0]))
print('# Minimum hue difference: {}'.format(scheme[1]))
print('# Hues: {}'.format(' '.join(map(str, hues))))
for i in range(n):
color_str = color_to_str(scheme[2][i][1])
print(f'Color {i}: {color_str}')
def grouper(iterable, n, fillvalue=None):
"""Collect data into fixed-length chunks or blocks."""
# Source: https://docs.python.org/3/library/itertools.html#recipes
# grouper('ABCDEFG', 3, 'x') --> ABC DEF Gxx"
args = [iter(iterable)] * n
return zip_longest(*args, fillvalue=fillvalue)
if __name__ == "__main__":
start_time = datetime.utcnow()
processes = cpu_count()
manager = Manager()
# Compile list of hues, optionally including highlight hue
if highlight:
hues = range(highlight, highlight + 360, hue_step)
hues = sorted([hue if hue < 360 else hue - 360 for hue in hues])
else:
hues = range(0, 360, hue_step)
# Compile list of potential colors as (hue, LabColor) pairs
colors = manager.list()
with Pool(processes) as pool:
colors = pool.map(convert_hue, hues)
pool.close()
pool.join()
colors.sort()
print('Colors prepared')
# Calculate Delta E between all colors
deltas = manager.dict()
with Pool(processes) as pool:
pool.map(calculate_delta, combinations(colors, 2))
pool.close()
pool.join()
# Making a dictionary now from multiprocessing.managers.DictProxy will
# increase subsequent performance a lot
deltas = dict(deltas)
print('Color deltas calculated')
# Compile list of potential schemes with n colors each
schemes = combinations(colors, n)
total_schemes = int(
factorial(len(colors))
/ (factorial(n) * factorial(len(colors) - n)))
print('Total schemes: {}'.format(total_schemes))
# Discard schemes if they contain hues that are too similar or if their
# Delta E of any two colors is too low
current_min_delta = Value('f', 0)
processed = Value('i', 0)
lock = Lock()
schemes_checked = []
# Process all other schemes
with Pool(processes) as pool:
if load_schemes_into_ram:
schemes_checked.extend(pool.map(check_scheme, schemes))
else:
# Chunks of 500000 have been fastest in my testing, but it probably
# depends on the number of schemes
# (Note that there is some overhead for the last chunk because it
# gets filled with None values to reach the chunk size)
for chunk in grouper(schemes, 500000):
schemes_checked.extend(pool.map(check_scheme, chunk))
pool.close()
pool.join()
# Remove None values and sort schemes by their minimum Delta E
schemes_checked = sorted([scheme for scheme in schemes_checked if scheme],
key=lambda x: x[0], reverse=True)
elapsed = datetime.utcnow() - start_time
print('Total time: {}'.format(str(elapsed).split('.')[0]))
# Output optimal color schemes
print('=====================')
print('Optimal color schemes')
print('=====================')
last_delta = None
for scheme in schemes_checked:
if last_delta and scheme[0] < last_delta:
break
output_scheme(finalize_scheme(scheme))
last_delta = scheme[0]